File Export Dialog
From Audacity Manual
The Export File dialog lets you specify folder location, file name and format (Save as type) for your exported file.
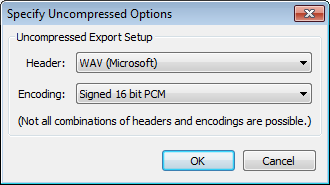
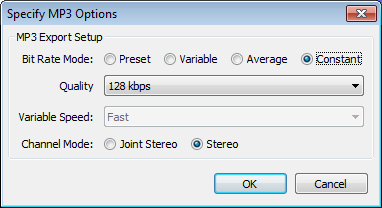
The Options button opens another dialog for making settings like quality or Encoding for formats with options. Here are examples for the Uncompressed and MP3 formats:
Always select the "Save as type" before clicking the Options button.
For details about the available options for each format click its link in the following list of "Save as types":
- Other uncompressed files -- includes all the uncompressed audio formats that Audacity can export.
- AIFF (Apple) signed 16 bit PCM and WAV (Microsoft) signed 16 bit PCM -- there are no options for the AIFF 16 bit and WAV 16 bit file types. WAV and AIFF can both be opened on either Windows or Mac computers. Both WAV and AIFF are lossless. Choose WAV or AIFF whenever you want to burn your exported file to an audio CD.
- GSM 6.10 WAV (mobile) -- this format has no options; it produces a WAV file encoded with the GSM 6.10 codec. This is a lossy voice codec producing small file sizes, used on GSM mobile digital telephone networks.
- MP3 Files -- to export the popular compressed, lossy MP3 format you will need to have downloaded the LAME MP3 encoder. You can then use the MP3 file type for a much smaller file than WAV or AIFF with some loss of audio quality. The format defaults to 128 kbps bit rate, giving you a file of about 1 MB per minute of audio.
- OGG Vorbis Files Ogg Vorbis -- a compressed, lossy format similar to MP3; it offers higher quality for the same file size but fewer applications can play this format.
- FLAC Files -- despite being compressed FLAC is lossless like WAV and AIFF. FLAC files are larger than MP3s and OGGs normally taking about 4 MB per minute of audio.
- MP2 Files MP2 -- a compressed, lossy format similar to MP3; it defaults to a 160 kbps bit rate. This produces comparable quality to 128 kbps MP3, but larger files. It is mainly used at higher bit rates in DVD soundtracks and radio broadcasting.
- (external program) -- sends audio via a command line to an external application either for processing or for encoding as a file. This is a method to export to an alternative MP3 encoder, or to a format not supported by Audacity.
- In FFmpeg-enabled builds, there will be a few additional export types available underneath "(external program)", marked with "(FFmpeg)". These are always present in FFmpeg-enabled builds of Audacity, but will only work if you install the FFmpeg libraries:
- AAC Files -- Advanced Audio Coding is a standardized, lossy compression and encoding scheme for digital audio. Designed to be the successor to the MP3 format, AAC generally achieves better sound quality than MP3 at similar bit rates.
- AC3 Files -- the common name used for the codec used in Dolby Digital.
- AMR Files -- the Adaptive Multi-Rate (AMR or AMR-NB) audio codec is a patented audio data compression scheme optimized for speech. AMR is also a file format for storing spoken audio using the AMR codec. Many modern mobile telephone handsets will allow you to store short recordings in this format.
- WMA Files -- Windows Media Audio (WMA) is an audio data compression technology developed by Microsoft. The name can be used to refer to its audio file format or its audio codecs. It is a proprietary technology that forms part of the Windows Media framework.
- Custom FFmpeg Export -- available in FFmpeg-enabled builds.